Position : Home > KNOWLEDGE CORNER > The absorption of Fish scale is better than fish skin or porcine skin
We compared quantity and structures of food-derived gelatin hydrolysates in human blood from three sources of type I collagen in a single blind crossover study. Five healthy male volunteers ingested type I gelatin hydrolysates from fish scale, fish skin, or porcine skin after 12 h of fasting. Amounts offree form Hyp and Hyp-containing peptide were measured over a 24-h period. Free Form Hyp and Hyp-Containing Peptide Levels in Plasma. The result as bellowing:
The amount of free form Hyp in plasma after administration of gelatin hydrolysate is shown in Figure 1A. Only negligible amounts of free form Hyp were observed before the administration of gelatin hydrolysate. In all subjects, free form Hyp in the plasma increased significantly after oral ingestion and reached a maximum 1 to 2 h after administration. The amount of free form Hyp in the fish scale group was significantly higher than that in the fish skin group 2 and 7 h after administration. The amount of free form Hyp in the porcine skin group was also significantly higher than that in the fish skin group 2, 4, and 7 h after administration. The amount of Hyp-containing peptide in plasma after administration of gelatin hydrolysate is shown in Figure 1B. Hyp-containing peptide was present in negligible amounts before administration. In almost all subjects, Hyp-containing peptides increased significantly after administration and reached maxi-mum levels 2 h afterward. The amount of Hyp-containing peptide in the fish scale group was significantly higher than that in both the fish skin and porcine skin groups 1 and 2 h after administration. The amount of Hyp-containing peptide in the porcine group was significantly higher than that in the fish skin group 2 h after administration. The fish scale group had a significantly higher amount of Hyp-containing peptide than the fish skin group 4 h after administration. In all subjects, the Hyp-containing peptide level returned to the initial zero level 7 h after administration.
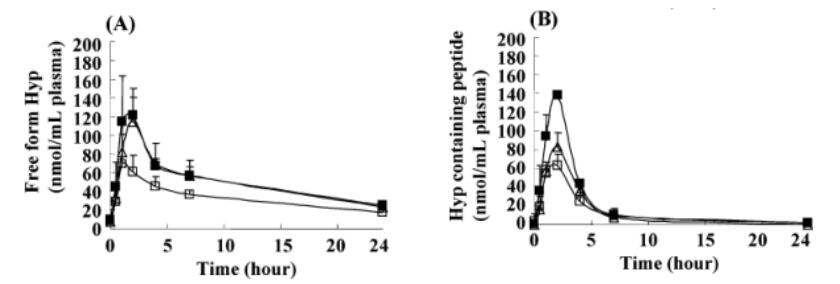
Figure 1. Amount of free form Hyp and Hyp-containing peptide in plasma after oral ingestion of fish scale (■), fish skin ( □ ), and porcine skin ( ∆ ) gelatin hydrolysates. (A) Amount of free form Hyp in plasma (nmol/mL). (B) Amount of Hyp-containing peptide in plasma (nmol/mL). Data are presented as the mean ± S.D., n ) 5. Statistical evaluation was analyzed by one-way ANOVA with a multiple-comparison test of Dunnet and a Tukey post hoc test
Mark:
Derived from Food and Health R&D Laboratories, Meiji Seika Kaisha, Ltd., 5-3-1, Chiyoda, Sakado-shi, Saitama 350-0289, Japan, and Department of Food Sciences and Nutritional Health, Kyoto Prefectural University, 1-5 Shimogamo, Kyoto 606-8522, Japan.
Copyright Hangzhou Nutrition Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Keywords: collagen manufacturer | collagen powder | collagen peptide | beauty collagen